1. Introduction to Single-Drum Dryer
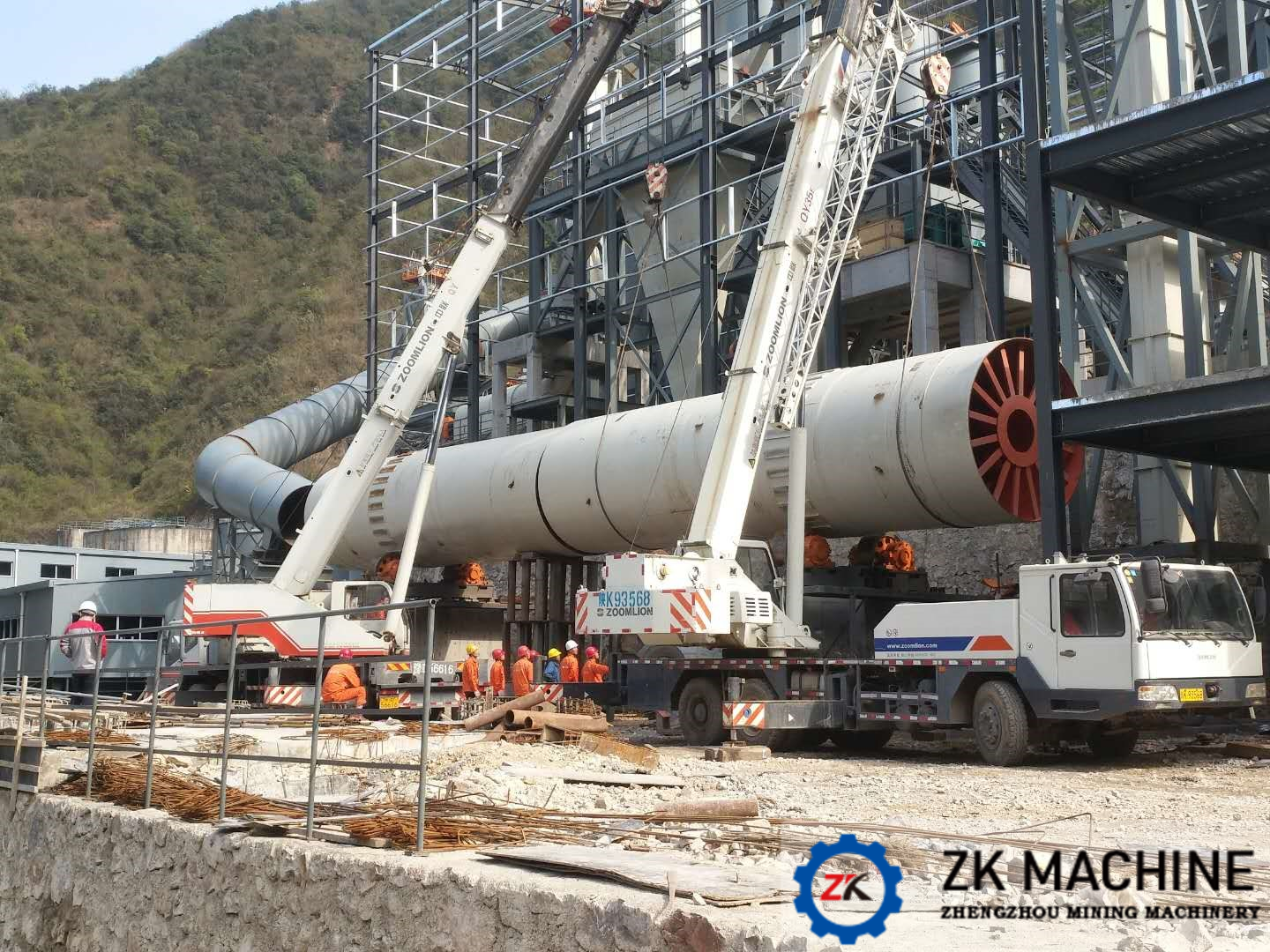
The single-drum dryer, as an indispensable drying equipment in modern industrial production, plays a critical role in industries such as building materials, metallurgy, and chemical engineering due to its high efficiency, energy-saving features, and strong adaptability. Through the synergistic action of the rotating drum and lifting plates, the device achieves efficient heat exchange between materials and hot air. Its technological evolution is closely aligned with market demands, making it a key driver for the intelligent and green transformation of industrial drying processes. This article systematically analyzes the core value and future prospects of single-drum dryers from the perspectives of technical principles, equipment structure, application scenarios, and development trends.
2. Definition and Core Functions of Single-Drum Dryer
A single-drum dryer is a horizontal rotary drying device that uses the drum's rotation to lift and disperse materials via lifting plates, ensuring full contact with hot air for rapid moisture evaporation. Its core functions include:
High-Efficiency Drying: Adopts a co-current heating method with thermal efficiency reaching 70%-85%, reducing drying time by 30%-50% compared to traditional equipment.
Flexible Capacity: Handles a processing capacity of 2-46 t/h per unit, meeting demands from small workshops to large-scale industrial production.
3. Hot Air System Design
3.1 Heat Source Compatibility: Supports multiple heat sources, including coal, gas, and oil, with controllable hot air temperatures ranging from 300-800°C.
3.2 Airflow Balance: Adjusts the inlet-to-outlet air ratio via control valves to optimize drying efficiency and energy consumption.
3.3 Dust Recovery: Combines cyclone and bag dust collectors, ensuring exhaust dust content remains below 30 mg/m³ to comply with environmental standards.
4. Key Parameter Influences
4.1 Relationship Between Rotation Speed and Retention Time: Every 1 rpm increase in speed reduces material retention time by 10%-15%.
4.2 Relationship Between Air Temperature and Drying Rate: Every 50°C increase in air temperature improves drying rate by 20%-30%.
4.3 Optimization of Lifting Plate Angle: A 45°-60° angle achieves optimal material dispersion and lifting height.
5. Core Components
5.1 Supporting Device: Bears the weight of the drum and materials, requiring a design that balances stability and maintenance convenience.
5.1.1 Number of Supports: Multiple support points ensure parallel contact between the rollers and drum tires along the axis, distributing weight evenly to enhance stability and reduce vibration.
5.1.2 Roller Structure: Rollers feature moderate diameter and width, supported by rolling bearings for low friction coefficients, reducing energy loss and facilitating maintenance.
5.1.3 Tire Clearance: A gap between the tire and drum allows for thermal expansion, preventing jamming while maintaining a secure fit.
5.2 Sealing System: Prevents hot air leakage and dust spillage, with structural features including:
5.2.1 Seal Type: Combines heat-resistant steel shingle seals with labyrinth seals for minimal air leakage.
5.2.2 Seal Placement: Seals are installed at both the feed and discharge ends, with an additional dust cover at the discharge end.
5.2.3 Adjustment Mechanism: Shingle seals use spring tensioning for automatic compensation, ensuring consistent sealing contact.
6. Application Prospects
As a core equipment in industrial drying, the single-drum dryer's technological advancements remain synchronized with industry needs. In the future, deeper integration with intelligent and green technologies will unlock greater value in fields like new energy materials and biomass energy. Enterprises must seize opportunities in technological innovation and market expansion, driving industry upgrades toward high-end and intelligent solutions through integrated system offerings.