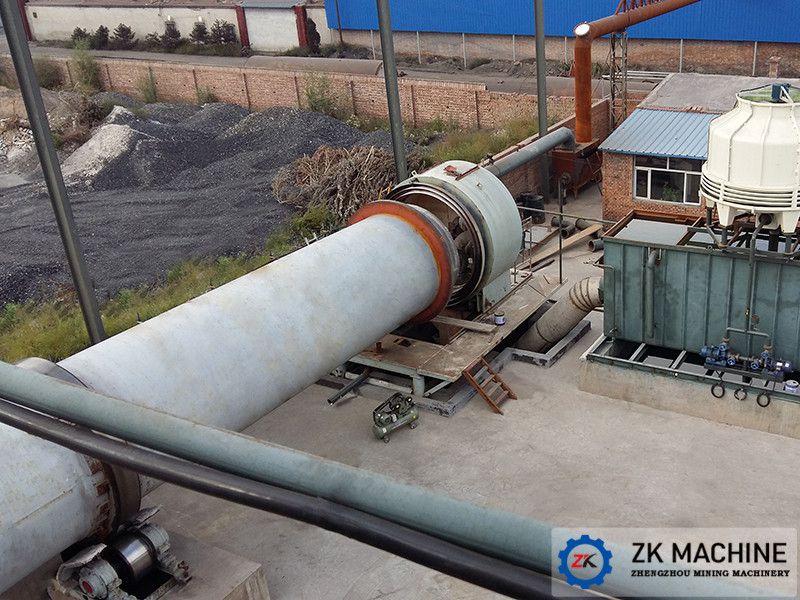
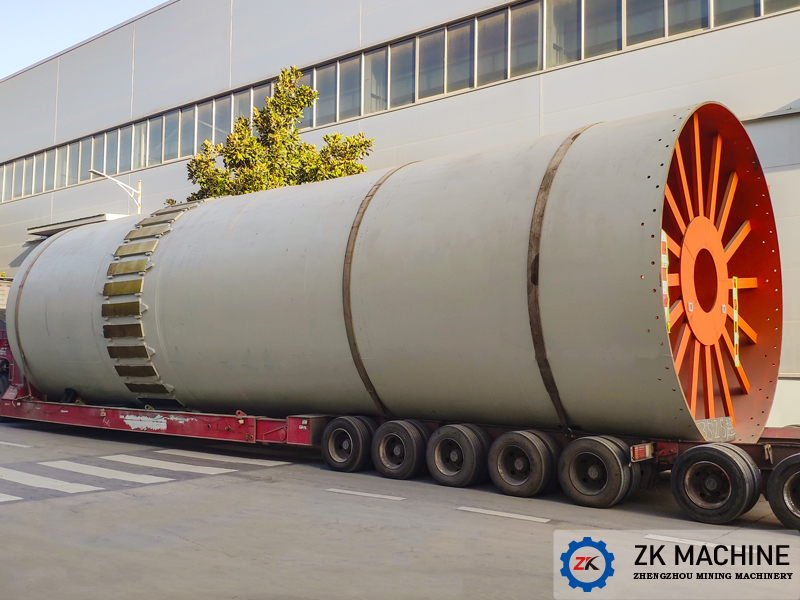
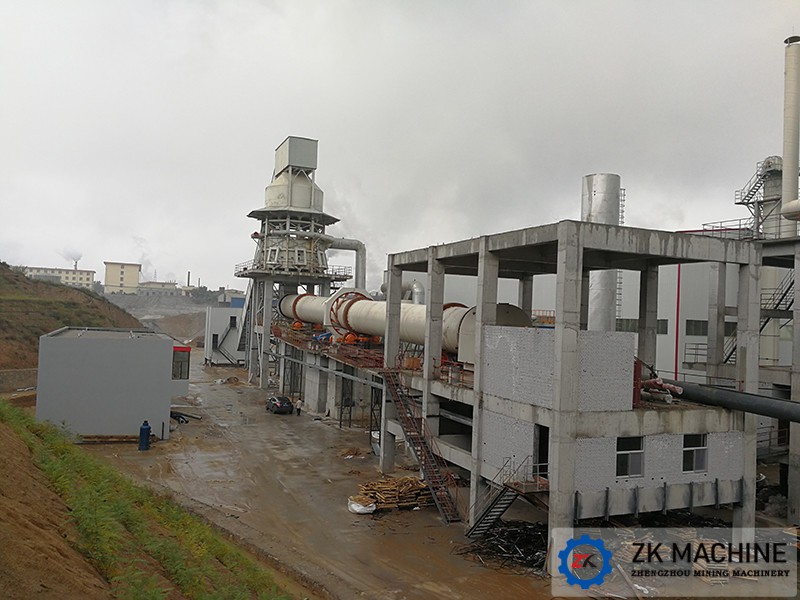
Kaolin rotary kiln is an important equipment in kaolin production and sintering. Generally, the temperature of the rotary kiln is required to reach above 950. Kaolin rotary kiln is also called kaolin calcining kiln. It can also be used for bauxite calcination, magnesium oxide calcination, zinc oxide calcination, etc.
Our company's kaolin rotary kiln is divided into eleven models according to the specifications of the cylinder, ranging from Ø1.6×32m-Ø4×80m. Cylinders with a diameter of 2.2m or more (including 2.2m) are equipped with auxiliary transmission, and those with a diameter of 3.0m or more (including 3.0m) are equipped with four groups of supports instead of three groups. The kiln speed is 0.58-2.85r/min, the slope is 3.5-4.0%, and the main motor power is 18.5kW-355kW, which can meet the calcination needs of kaolin mineral products in the range of 2t-20t per hour.
✔ Application
Kaolin rotary kilns are primarily used to produce calcined kaolin, which finds applications across multiple industrial sectors such as paper, coatings, rubber and plastics, ceramics, and cosmetics.
✔ Advantages
1. The external structure of the kaolin rotary kiln is simple and the internal structure is reasonable, which is easy to install, operate and maintain;
2. The cylinder in the kiln runs very evenly, with low heat loss, low power consumption and low failure rate. It not only effectively realizes the recycling of heat energy, but also reduces production costs;
3. The sealing inside the kiln is relatively reasonable, which effectively prevents the entry of foreign matter and cold air from the outside, and also reduces the overflow of dust, reduces dust pollution and improves the production environment;
4. The equipment is equipped with an automatic cooling device. The calcined kaolin will automatically enter the cooling device to achieve automatic cooling, which can effectively improve the recycling rate of kaolin materials and increase product output
✔ Working principle
When the kaolin rotary kiln starts to work, the kaolin raw material enters the cylinder through the preheater from the end of the kiln. Due to the inclined installation of the cylinder and the slow rotation, the kaolin material produces a roll in the circumferential direction and from the axial direction. A compound movement in which the higher end moves toward the lower end. The kaolin material is decomposed and fired in the kiln, and the clinker is discharged from the kiln head (lower end) and enters the cooler.