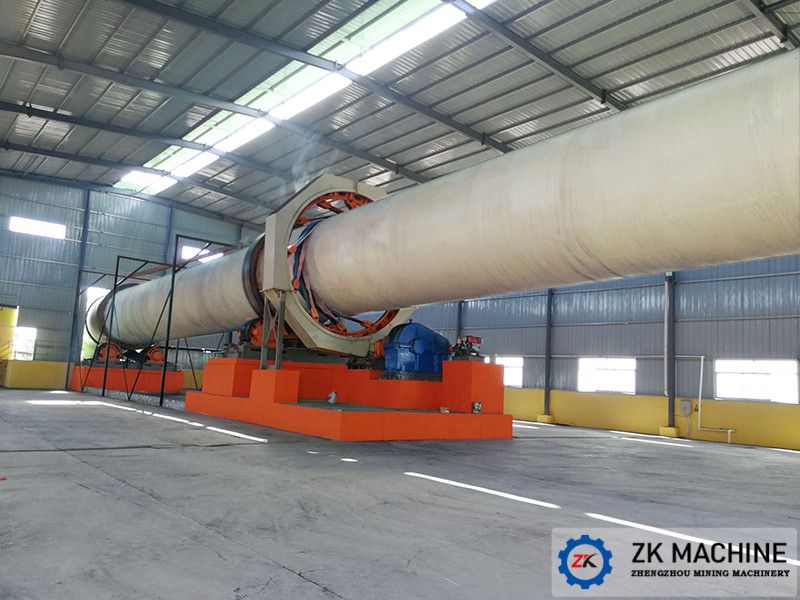
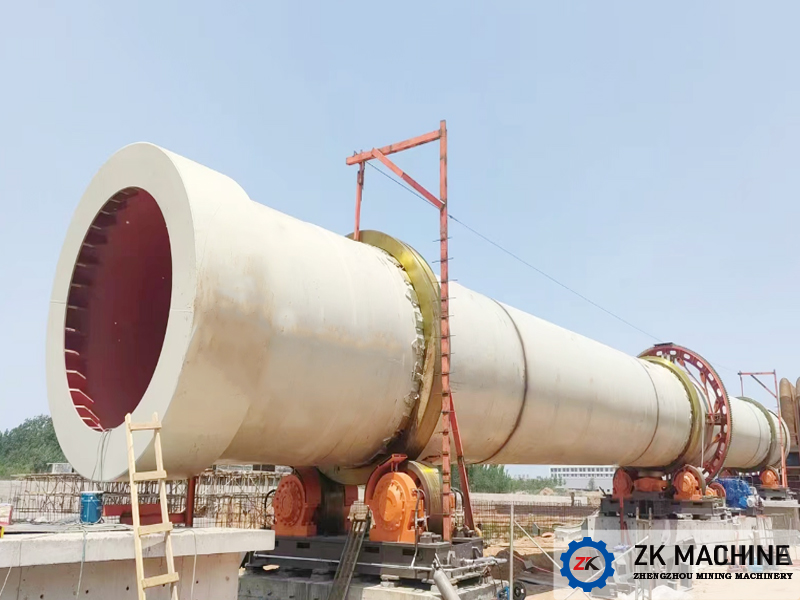
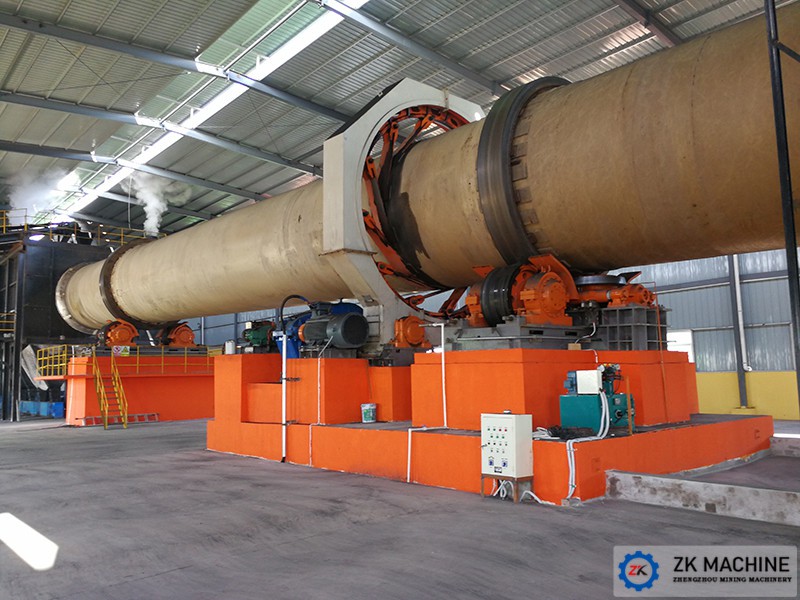
Zinc oxide is a fine powder and is widely used in rubber, medicine, printing and dyeing, optics and other fields. The zinc oxide rotary kiln is one of the most common and efficient methods for processing zinc-containing intermediate materials, and is the core roasting equipment for zinc calcination. ZK Machinery’s zinc oxide rotary kiln is expertly engineered for high-yield production, particularly suitable for industry-proven methods like the Waelz process.
Our zinc oxide rotary kiln products have eight models with different cylinder specifications. The cylinder diameter and length range from φ1.2×18m to φ5×80m, and the kiln slope is 3%-4%. According to customer needs, we can design a complete zinc oxide production line with a daily processing capacity of 0.5~1500t/d.
✔ Application Fields
The zinc oxide rotary kiln is primarily used for the reduction roasting of zinc-containing wastes to recover zinc oxide. It is the ideal equipment for processing steel plant dust and other secondary zinc materials, forming the heart of efficient recovery systems such as a Waelz process plant.
✔ Calcination Materials
zinc concentrate, zinc-containing sludge, zinc-containing tailings, steel plant dust ash, steel plant flue ash, zinc-containing flue ash, zinc-containing dust mud, blast furnace secondary ash, converter secondary ash, electric furnace dust ash (EAF dust), steelmaking LT ash, converter OG mud, blast furnace gas mud, blast furnace gravity ash, etc.
✔ Advantages
1.The kiln system features a simple configuration, which reduces initial investment and enhances operational productivity;
2.It delivers high processing efficiency. The resulting zinc oxide is of high purity with a low rate of nodulation;
3.The entire production line operates stably with high output, while optimized thermal design significantly lowers fuel consumption;
4.With minimal equipment requirements, each component in the line performs at its best, ensuring a rational and cost-effective investment for our customers.
✔ Working Principle
Zinc oxide rotary kiln working principle is the whole process and principles of the calcined zinc, zinc-containing materials. Generally it adopts the zinc oxide rotary kiln to process of the zinc-containing filter cake. The zinc in the filter cake mainly exists in the form of zinc ferrite, oxide and sulfate. Under the high temperature in the rotary kiln, the zinc ferrite and solid carbon will produce the reaction for oxide-reduction, then it will get the zinc, at the same time lead and cadmium sulfate also be reduced, will volatilize in the form of sulfide and gold bucked out. The reduced and volatilized metal from the solid phase will be re-oxidation, and finally will be produced in the form of oxide.
Note: The amount of air into the zinc oxide rotary kiln should ensure that the flue gas has sufficient oxygen to re-oxidize all the metal vapor, sulfide and carbon monoxide. Increasing the amount of air in the zinc oxide rotary kiln will increase the recovery zone to the feed end. On the contrary reducing the amount of air, the reduction area is shortened and the starting section of the reduction zone extends toward the discharge end.